Mitigate Pain Clinic – Dr Jeshnu Tople – Pain Management Specialist In Nagpur
Buttock Pain
Buttock Pain Treatment
Understanding the Buttock Area
- ccupational Therapy: For individuals who have difficulty performing daily tasks due to buttock pain.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Counseling on improving posture or workplace ergonomics to avoid further strain on the gluteal region.
Common Causes of Buttock Pain

1. Coccydynia (Tailbone Pain)
Symptoms:
- Pain localized at the base of the spine, particularly when sitting
- Tenderness and discomfort when pressing on the tailbone
- Sharp pain when sitting or transitioning from sitting to standing
Treatment Options:
- Conservative care: Physiotherapy, medicines, posture adjustments, and using cushioned seats.
- Interventional pain management: Ganglion impar block or radiofrequency ablation, as offered at Mitigate Pain Clinic.
2. Piriformis Syndrome
Symptoms:
- Pain that radiates from the buttock to the back of the leg (similar to sciatica)
- Pain worsens with prolonged sitting or physical activities
- Muscle tightness or spasms in the buttock area
Treatment Options:
- Stretching and physical therapy: Exercises that target the piriformis muscle to alleviate tension.
- Trigger point injections: To reduce inflammation and muscle spasms.
- Nerve blocks: Mitigate Pain Clinic offers nerve block injections to relieve sciatic nerve compression.
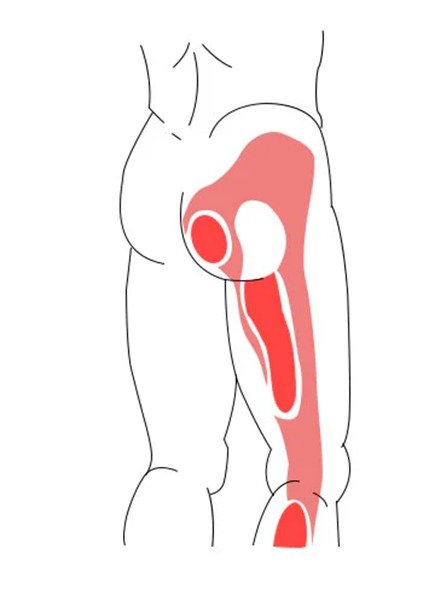
3. Gluteal Myofascial Pain
Symptoms:
- Deep, aching pain in the buttock muscles
- Muscle tightness and limited range of motion
- Pain worsens with prolonged sitting or standing
Treatment Options:
- Trigger point injections: Mitigate Pain Clinic provides injections to release tight muscles and reduce pain.
- Physical therapy: Stretching and strengthening exercises help alleviate muscle tension.
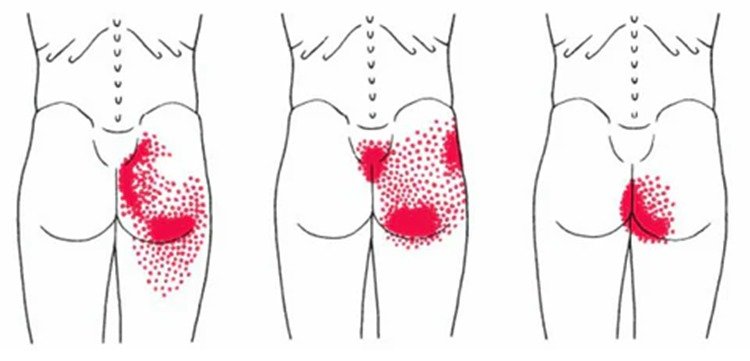
4. Bursitis (Ischial Bursitis)
Symptoms:
- Pain in the lower buttock area, especially when sitting
- Swelling and tenderness in the affected area
- Stiffness or limited movement in the hip joint
Treatment Options:
- Anti-inflammatory medications: NSAIDs can reduce inflammation.
- Platelet rich plasma (PRP) injections: These reduce inflammation and provide long-term relief.
- Rest and ice therapy: To relieve swelling and pain in the bursae.
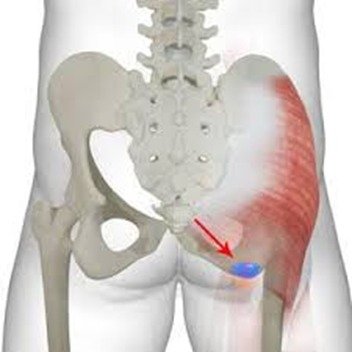
5. Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
Symptoms:
- Pain in the lower back and buttocks, especially when sitting or lying in lateral decubitus position
- Stiffness in the hips or pelvis
- Pain radiating down one or both legs
Treatment Options:
- SI joint injections: These are administered to reduce inflammation and pain at the sacroiliac joint.
- Physical therapy: To improve joint alignment and mobility.
- Radiofrequency ablation: This technique, offered at Mitigate Pain Clinic, targets the nerves in the SI joint to block pain signals.

6. Hip Joint Problems
Symptoms:
- Pain in the groin or buttock area, especially when moving the hip
- Stiffness or reduced range of motion in the hip joint
- Clicking or popping sounds when moving the hip
Treatment Options:
- Hip joint injections: PRP or hyaluronic acid injections can help relieve inflammation and restore mobility.
- Physical therapy: Strengthening the muscles around the hip to improve joint stability.
- Surgical intervention: In severe cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to address hip joint issues.
Diagnosing Buttock Pain at Mitigate Pain Clinic
At Mitigate Pain Clinic, we take a comprehensive approach to diagnosing the underlying cause of your buttock pain. During your initial consultation, we will perform a thorough evaluation, including:
Medical history: We assess your symptoms, previous injuries, and daily habits that may contribute to pain.
Physical examination: Our specialist will evaluate the affected area to identify signs of inflammation, tenderness, or muscle tension.
Imaging tests: X-ray, MRI, USG or CT scans may be used to diagnose structural issues.
A proper diagnosis is key to developing a personalized treatment plan that targets the root cause of your pain.
Preventing Buttock Pain
- Maintain good posture: Sit upright with proper back support to reduce strain on the gluteal muscles and coccyx.
- Use proper seating: For extended periods of sitting, use cushioned seats or ergonomic chairs.
- Stretch regularly: Regular stretching of the gluteal muscles, hip flexors, and lower back can prevent tightness and pain.
- Stay active: Incorporate regular exercise into your routine to strengthen the muscles around the buttock, pelvis, and hips.
Why Choose Mitigate Pain Clinic for Buttock Pain Treatment?
At Mitigate Pain Clinic, we pride ourselves on offering personalized care using the most advanced pain management techniques available. Our team of specialists is committed to helping you find lasting relief from chronic buttock pain.
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Our Treatments
- Joint Pain
- Back Pain
- Sciatica Pain
- Neck Pain
- Hand Pain
- Shoulder Pain
- Foot & Ankle Pain
- Limb Pain
- CRPS Pain
- Cancer Pain
- Headache
- Hyperhidrosis
- Herpes Zoster Pain
- Chronic Pelvic Pain
- Scar Tenderness
- Postherpetic Neuralgia
- Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Peripheral Neuralgia
- Chronic Vascular Pain
- Generalised Body Pain
- Chronic Injury Pain
- Failed Back Surgery Syndrome
- Chronic Post Surgical Pain
- Other Painful Conditions
- Slipped DISC / PIVD